Choline is an essential nutrient during pregnancy as it can help protect a newborn against neural tube defects while boosting the mother’s brainpower.
Choline is a dietary component responsible for maintaining healthy cell membranes and brain function. It is important for expecting mothers as choline protects newborns from neural tube defects – for instance, defects on the spine, brain or spinal cord. Studies also suggest that adequate choline during pregnancy has lifelong effects on a baby’s ability to learn and remember, and may even deter mental illness. Other benefits for mothers who have sufficient choline include a reduced risk of breast cancer and lower levels of homocysteine, and increased brainpower.
The recommended daily dose of choline for pregnant women is 450mg, while women who are nursing should take 550mg of choline. Your need for choline may increase during pregnancy as your baby draws on your supply.
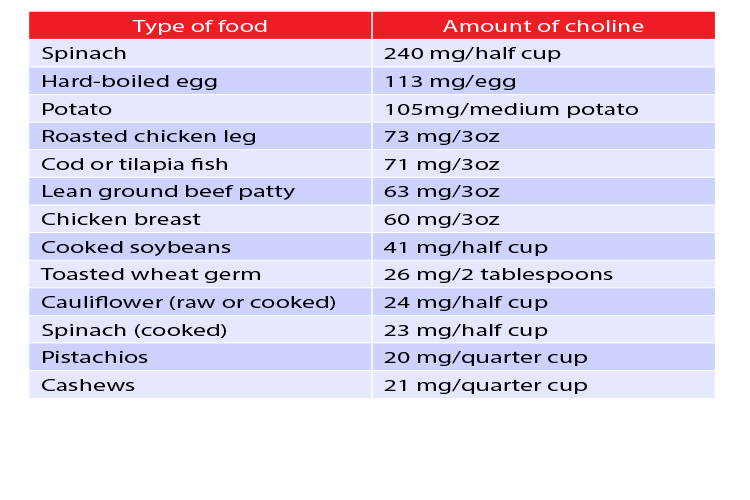
For mothers who breastfeed, by including choline in a lactating mother’s diet, the baby will be able to get its primary source of choline from breast milk. Although the human body is capable of producing choline, it is mostly obtained through a healthy diet. This includes eating foods like liver, eggs, breast milk and other choline-rich foods. Examples of food rich in choline are:
It is also possible to get too much choline. This is usually caused by excessive intake of choline from supplements. Choline toxicity can cause you to have a fishy body odour, vomiting, diarrhea and decreased blood pressure. Thus, food sources and modest amounts of prenatal vitamins are the safest way to include choline in your diet when you are pregnant.
DID YOU KNOW?
Choline as a stress reliever: A recent study found an interesting effect of high choline intake during pregnancy. The nutrient appears to decrease the baby’s cortisol levels, which is known as the hormone that causes stress. This might help to lessen the effect of a pregnant mother’s stress on the baby’s developing brain, nervous system, and metabolism.
















